Basic Knowledge of SMD Chip for Newcomers to LED Lighting
SMD stands for Surface Mounted Device and is currently the most welcomed LED package type. SMD LED lights are produced by using surface mounted technology (SMT) to mount SMD chips on printed circuit boards (PCB).
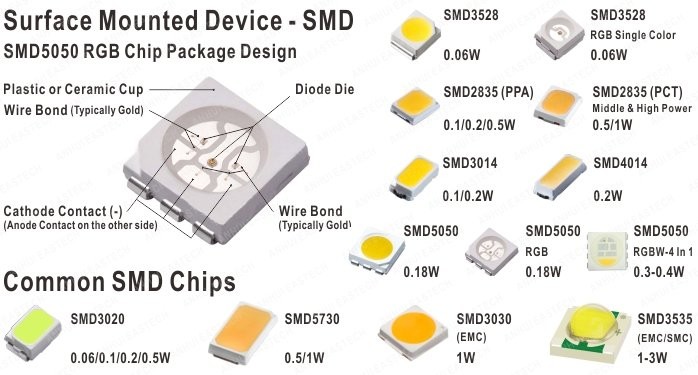
SMD chips are designed to a variety of flat-square shapes and sizes, which have many types. The most common types of SMD chips are: 3528, 5050, 2835, 3014, 4014, 3020, 5730, 3030 and 3535. The number indicate the chip size, for example, 3528 is for the chip with size 3.5 x 2.8mm. (some of SMD chips can be made with very small size and can be used as indicator lights of cell phones and laptop computers. The little light of cell phone which stays on after the screen turns off is powered by a small SMD chip.)
SMD chip is a very important development for the LED industry because of the ability to put 3 diodes on the same chip. When a chip includes a red, green and blue diode, then it has RGB ability and can create any color you want by adjusting the level of output from each individual diode on the chip. If the chip with 3 same diodes, it will increase the output lumen. For example, 3528 has only one diode, while 5050 has 3 diodes on its chip, thus 5050 has the RGB ability on the single chip and 3 times output lumen of 3528. (4 in 1 designed 5050 has RGB+W ability and 4 times output lumen of 3528.)
Unlike only two contacts designed for DIP chip, SMD chips may have 2, 4 or 6 contacts (called pins), which depends on the quantity of diodes on the SMD chips. For SMD chip, there is an individual circuit for each diodes and each individual circuit is designed with 2 pins. For example, 5050 has 3 diodes on its chip, thus it has 6 pins. (5050 RGB+W type gets 4 diodes with total 8 pins.)
The power consumption (W) and output lumen (LM) comparison of each SMD chip is listed as the following chart:
SMD Chip Power Consumption (W/PC) & Output Lumen (LM/PC)
3528 0.06W, 6 - 9LM, always designed for low power purpose
5050 0.18W, 18 - 27LM, mainly designed for low power purpose
But currently middle power (0.5W) and high power (1-3W) have been developed, especially for RGB and RGB+W type
2835 0.1W, 10 - 15LM;
0.2W, 20 - 30LM, for low power purpose
0.5W, 50 - 65LM, for middle power
1W, 100 - 130LM, for high power
3014 0.1W, 9 - 13LM;
0.2W, 18-24LM, always for low power purpose with high bright feature
4014 0.2W, 24 - 26LM, always for low power purpose
3020 0.06W, 7 - 8LM;
0.1W, 9 - 11LM;
0.2W, 18 - 24LM, for low power purpose
0.5W, 50 - 60LM, for middle power purpose always with EMC reflector
5730 0.5W, 45 - 60LM, main for middle power purpose
1W, 90 - 120LM, for high power
3030 1W, 100 - 130LM, always for high power purpose
3535 1 - 3W, - LM, always for high power purpose with EMC or SMC reflector
You can easily calculate the power and output lumen of SMD LED lights through above chart. This chart for the various types of SMD chips and their correct lumen,but LED technology is developing, the data may be changed in near future.
From the chart, according to the power consumption (W/PC), SMD chips can be divided into 3 classes which are low power (<0.5W/PC), middle power (0.5-1W) and high power (>1W). For the SMD chip, the higher the power is, the more heat it will dissipate and the higher the temperature it will be when working. Then the higher temperature the reflector of SMD chip can resist, the longer life-span SMD chip will get. Thus the quality of reflectors greatly affects the life-span of SMD chip. Therefore different reflectors are needed for different power levels. The main reflector materials for SMD chips are PPA (Polyphthalamide), PCT (Polycyclohexylene-dimethylene Terephthalates), EMC (Epoxy Molding Compound) & SMC (Silicone Molding Compound).
The comparison of these 4 reflectors is list as the following chart:
PPA - Thermoplastic
Advantage: High brightness = 95%, Good moldability, Cheaper material cost
Disadvantage: Poor resistance of heat and light
Operating Power (W/PC): <0.5W
PCT - Thermoplastic
Advantage: Good resistance of heat and light, Good reliability, High brightness = 97%
Disadvantage: Slightly expensive material cost, Poor moldability
Operating Power (W/PC): 0.5 - 0.8W
EMC - Thermosetting
Advantage: Excellent resistance of heat and light, Excellent reliability, Initial brightness = 94.8%
Disadvantage: Expensive material cost, Transfer molding
Operating Power (W/PC): 0.2 - 1.5W
SMC - Thermosetting
Advantage: Excellent resistance of heat and light, Excellent reliability, Good adhesion with silicone, High brightness = 97%
Disadvantage: Much more expensive material cost, Transfer molding
Operating Power (W/PC): >1.5W
Many engineers lower the power (reduce the standard current of LED chip), as a result, the lumen of each chip will be reduced accordingly, how to have the same or even higher total output lumen of LED lights? The solution is to increase the quantity of chips. (See below example)
For example: standard SMD2835 (0.2W) chip @ 25LM
10 PCs standard SMD2835 (0.2W) chip LED
Power: 2W
Lumen: 250LM
If we lower the power to half (by reduce the current): 0.1W per chip
Now: 10 Pcs lower power SMD2835 (0.1W) chip
Power: 1W
Lumen: 150LM (60% of standard lumen, usually, reduce half of the power doesn't mean half of the lumen disappeared, why? Because LED has higher luminious efficacy when in lower current.)
If we increase the quantity of lower power SMD chip 2835 (0.1W) to 20pcs (The current for each chip is the same)
Power: 2W
Lumen: 300LM
You will easily find that the lumen is higher though the total power is the same. (Because the light efficiency is higher)
Advantage: This is a solution that most of the engineers probably use to improve the light efficiency.
Disadvantage: However the cost of LED lights will be higher accordingly due to there needs more quantity of chips.
Note: The calculation based on the same input LED driver power supply, we assume the power efficiency is the same.
The features of SMD chips:
High brightness
Based on the same power consumption, SMD chip produces the highest brightness among other types of LED packages such as DIP, high power, COB and MCOB chip. In other words, the light efficiency of SMD chip is the highest and the best.
Better for thermal management
The SMD chip produces very little heat while has relatively high output lumen, because it is driven by a low voltage and current. Unlike the high power chip or COB chip, which usually produce much more heat at just one point, it is difficult to conduct the heat, SMD chip can be placed separately among the light body, and can be designed as a light surface with many chips.
SMD chip performs better in thermal management, in a result that the rate of light decay is much lower and make the initial brightness (output lumen) stay in a longer time.
Competitive price
It is no doubt that SMD chip is much lower in price that high power or COB, that is one of the important reason more and more LED products adopt SMD chip.
Application of SMD chip
Due to the RGB ability and brightness of SMD chip, these chips are used extensively for all kinds of LED lights. The lower power ones can be made for LED bulb, strip light, corn light, spotlight, tube light, panel etc. While the high power ones can be made for industrial lights such as high bay, track light, flood light, street light etc.
SMD chip is the most popular LED type nowadays. It is commonly applied in both residential and commercial LED lighting products.
Robert Sun
GM of Anhui Eastech
Email: r.sun@ilampplus.com
www.ilampplus.com