Abstract
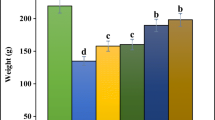
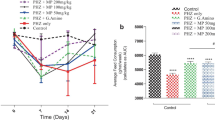
There are many medicinal plants in traditional medicine which are used to prevent, control, and treat anemia. One of these plants is Allium saralicum R.M. Fritsch. The purpose of our research was to investigate the effect of aqueous extract of A. saralicum leaf in the treatment of hemolytic anemia. In this study, 60 rats were used. Induction of hemolytic anemia was done by three injections of Phenylhydrazine in 50 animals. Then, the rats were divided into six subgroups, including negative healthy control, untreated negative control, and four groups receiving the A. saralicum at 25, 50, 100, and 200 mg/kg concentrations. At the end of day 15 of treatment, the animals of all groups were weight and then sacrificed. The blood, liver and spleen samples were drawn immediately to analyze the hematological, biochemical and histological parameters. All groups of A. saralicum (especially AS200) significantly (p ≤ 0.05) reduced the raised concentrations of Fe, ferritin, erythropoietin, ALP, AST, ALT, GGT, cholesterol, LDL, triglyceride, total and conjugated bilirubin, urea, and creatinine and increased the levels of body weight, HDL, total protein, albumin, WBC, lymphocyte, monocytes, platelet, RBC, Hb, PCV, MCV, MCH, and MCHC as compared to the untreated group. Also, A. saralicum at all doses prevented pathological changes in the liver and spleen. In conclusion, because of aqueous extract of A. saralicum leaf anti-anemic property, it can be used as a medical supplement or drug.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bjelakovic G, Nikolova D, Simonetti RG, Gluud C (2004) Antioxidant supplements for prevention of gastrointestinal cancers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 364:1219–1228
Boretti FS, Buehler PW, D’Agnillo F, Kluge K, Glaus T, Butt OI, Jia Y, Goede J, Pereira CP, Maggiorini M, Schoedon G, Alayash AI, Schaer DJ (2009) Sequestration of extracellular hemoglobin within a haptoglobin complex decreases its hypertensive and oxidative effects in dogs and guinea pigs. J Clin Invest 119(8):2271–2280
Cheraghi M, Asadi-Samani M (2016) Hematopoietic medicinal plants based on ethnobotanical documents of Iran: a strategy to develop nature-based drugs effective on anemia. Pharm Lett 8(5):393–399
Diallo A, Gbeassor M, Vovor A, Eklu-Gadegbeku K, Aklikokou K, Agbonon A, Abena AA, de Souza C, Akpagana K (2008) Effect of Tectona grandis on phenylhydrazine-induced anaemia in rats. Fitoterapia 79(5):332–336
Farzaei MH, Zangeneh MM, Goodarzi N, Zangeneh A (2018) Stereological assessment of nephroprotective effects of Trachyspermum ammi essential oil against carbon tetrachloride-induced nephrotoxicity in mice. Int J Morphol 36(2):750–757
Goodarzi N, Zangeneh MM, Zangeneh A, Najafi F, Tahvilian R (2017) Protective effects of ethanolic extract of Allium Saralicum R.M. Fritsch on CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. J Rafsanjan Univ Med Sci 16(3):227–238
Goodarzi N, Zangeneh MM, Zangeneh A (2018) The effect of ethanolic extract of Allium saralicum R.M. Fritsch on diabetic hepatopathy in male mice. Sci Res J Shahed Univ 25:21–30
Goorani S, Koohi MK, Zangeneh A, Zangeneh MM, Moradi R (2018) Pharmacological evaluation of anti-anemic property of aqueous extracts of Falcaria vulgaris leaf in rats. Comp Clin Path. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-018-2839-6
Hamelian M, Zangeneh MM, Amisama A, Varmira K, Veisi H (2018) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Thymus kotschyanus extract and evaluation of their antioxidant, antibacterial and cytotoxic effects. Appl Organometal Chem 32(9):e4458
Han GH (2000) Antimicrobial food packaging. J Food Technol 54(3):56–65
Holley RA, Patel D (2005) Improvement in shelf life and safety of perishable foods by plant essential oils and smoke antimicrobials. J Food Microbiol 22(4):273–292
Lee HW, Kim H, Ryuk JA, Kil KJ, Ko BS (2014) Hemopoietic effect of extracts from constituent herbal medicines of Samul-tang on phenylhydrazine-induced hemolytic anemia in rats. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 7(9):6179–6185
McKie AT, Barrow D, Latunde DadaGO, Rolfs A, Sager G, Mudaly E, Mudaly M, Richardson C, Barlow D, Bomford A, Peters TJ, Raja KB, Shirali S (2004) Tissue specific changes in iron metabolism genes in mice following Phenylhydrazine-induced haemolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta 14(2):169–176
Onyeabo C, Achi NK, Ekeleme-Egedigwe CA, Ebere CU, Okoro CK (2017) Haematological and biochemical studies on Justicia carnea leaves extract in phenylhydrazine induced-anemia in albino rats. Acta Sci Pol Technol Aliment 16(2):217–230
Qaseem A, Humphrey LL, Fitterman N, Starkey M, Shekelle P (2013) Treatment of anemia in patients with heart disease: a clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med 159(11):770–779
Ryu JH, Yook CS (2001) The effects of sa-multang, a traditional chines medicine, on phenylhydrazine-induced anemic rats. J Appl Pharmacol 9:1–6
Sato H, Sakari T, Fujimura H, Sugimoto J, Kume E, Kitamura K, Takahashi K (2012) Hematological and morphological investigation of thrombogenic mechanisms in the lungs of phenylhydrazine treated rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol 65(4):457–462
Sayyedrostami T, Pournaghi P, Ebrahimi Vosta-Kalaeea S, Zangeneh MM (2018) Evaluation of the wound healing activity of Chenopodium botrys leaves essential oil in rats (a short-term study). J Essent Oil Bear Pl 21(1):164–174
Sherkatolabbasieh H, Hagh-Nazari L, Shafiezadeh S, Goodarzi N, Zangeneh MM, Zangeneh A (2017) Ameliorative effects of the ethanolic extract of Allium saralicum R.M. Fritsch on CCl4-induced nephrotoxicity in mice: a stereological examination. Arch Biol Sci 69(3):535–543
Shukla P, Yadav NK, Singh P, Bansode FW, Singh RK (2012) Phenylhydrazine induced toxicity: a review on its hematotoxicity. Int J Basic Appl Med Sci 2(2):86–91
Telford RD, Sly GJ, Hahn AG, Cunningham RB, Bryant C, Smith JA (2003) Footstrike is the major cause of hemolysis during running. J Appl Physiol 94(1):38–42
Zangeneh MM, Goodarzi N, Zangeneh A, Tahvilian R, Najafi F (2018a) Amelioration of renal structural changes in STZ-induced diabetic mice with ethanolic extract of Allium saralicum R.M. Fritsch. Comp Clin Path 27(4):861–867
Zangeneh MM, Zangeneh A, Salmani S, Jamshidpour R, Kosari F (2018b) Protection of phenylhydrazine-induced hematotoxicity by aqueous extract of Ocimum basilicum in Wistar male rats. Comp Clin Path. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-018-2845-8
Zangeneh MM, Zheleh M, Salmani S, Zangeneh A, Almasi M, Khedri MR, Rasidi K (2018c) Assessment of the anti-anemic effect of aqueous extract of Allium eriophyllum Boiss leaf in phenylhydrazine-treated Wistar male rats. Comp Clin Path. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-018-2851-x
Zhaleh M, Sohrabi N, Zangeneh MM, Zangeneh A, Moradi R, Zhaleh H (2018) Chemical composition and antibacterial effects of essential oil of Rhus coriaria fruits in the west of Iran (Kermanshah). J Essent Oil Bear Pl 21(2):493–501
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Kermanshah University of Medical Sciences for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical statement
All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed. All animal procedures were approved by standards of Payame Noor University of Kermanshah-Iran (No. 01/Z/G 1395/12/01) on Humane Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, in accordance with the Research Ethics Committee of the Ministry of Health and Medical Education in Iran (adopted on April 17, 2006), based on the Helsinki Protocol (Helsinki, Finland, 1975).
Conflict of interest
This manuscript described has not been published before; not under consideration for publication anywhere else; and has been approved by all co-authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goorani, S., Shariatifar, N., Seydi, N. et al. The aqueous extract of Allium saralicum R.M. Fritsch effectively treat induced anemia: experimental study on Wistar rats. Orient Pharm Exp Med 19, 403–413 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-019-00361-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-019-00361-5