Abstract
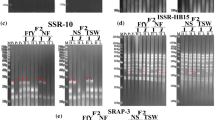
Plumbago auriculata Lam. is an ornamental plant native to South Africa and widely cultivated in China, but the cultivated plants are dominated by a single variety. The development of new varieties is of great commercial interest, and genetic diversity is the foundation of breeding programs. In this study, 85 progenies were obtained by crosses between Plumbago auriculata and Plumbago auriculata f. alba. The genetic diversity of these hybrids was evaluated using horticultural traits and ISSR and SRAP markers. Of the 25 horticultural traits evaluated, the largest variation was found in the beginning of the blooming period, and sepal length was the least variable trait. Correlation analysis showed that the wider the plant, the greater the number of inflorescences and the earlier the flowering. Seven factors explained 65.171% of the total variance; the first factor was leaf morphology, and the second factor was flower morphology. The genetic diversity of the 85 progenies was analyzed using seven pairs of SRAP primers and eight ISSR primers. The average number of effective alleles for 85 hybrids was 1.638, and the average Shannon index value was 0.507. The Nei genetic similarity coefficient indicated that the similarity between WLBS and WSBL was the highest, while that between BLWS and BSWL was the lowest. Analysis of molecular variance (AMOVA) indicated that the main variation was within populations. Cluster analysis based on horticultural traits and molecular markers divided all progenies into seven and five groups, respectively, and there were obvious differences between the two clusters. In this study, we created intermediate materials for future breeding, taking the first step in the cross-breeding of P. auriculata.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afkhami-Sarvestani R, Serek M, Winkelmann T (2012) Interspecific crosses within the Streptocarpus subgenus Streptocarpella and intergeneric crosses between Streptocarpella and Saintpaulia ionantha genotypes. Sci Hortic 148:215–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2012.10.006
Baliyan D, Sirohi A, Kumar M, Kumar V, Malik S, Sharma S (2014) Comparative genetic diversity analysis in chrysanthemum: a pilot study based on morpho-agronomic traits and ISSR markers. Sci Hortic 167:164–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2013.12.029
Barbosa DA, Silva GW, Silvia N, Toledo PMC, Alves RBR, Borges FT, Medeiros PPT (2018) Genetic diversity between and within full-sib families of Jatropha using ISSR markers. Ind Crop Prod 124:899–905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.08.066
Bhering LL, Peixoto LdA, Ferreira-Leite NLS, Laviola BG (2015) Molecular analysis reveals new strategy for data collection in order to explore variability in Jatropha. Ind Crop Prod 74:898–902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.06.004
De Souza EH, Versieux LM, Duarte SFV, Lanzoni RM, de Carvalho CMAP, Pinheiro MA (2017) Interspecific and intergeneric hybridization in Bromeliaceae and their relationships to breeding systems. Sci Hortic 223:53–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2017.04.027
Deshpande J, Labade D, Shankar K, Kata N, Chaudhari M, Wani M, Khetmalas M (2014) In vitro callus induction and estimation of plumbagin content from Plumbago auriculata Lam. Indian J Exp Biol 52:1122–1127
Dey SS, Singh AK, Chandel D, Behera TK (2006) Genetic diversity of bitter gourd (Momordica charantia L.) genotypes revealed by RAPD markers and agronomic traits. Sci Hortic 109:21–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2006.03.006
Doyle J (1991) DNA protocols for plants. Mol Tech in Tax 57:283–293. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-83962-7_18
Ferrero V, de Vega C, Stafford GI, Van Staden J, Johnson SD (2009) Heterostyly and pollinators in Plumbago auriculata (Plumbaginaceae). S Afr J Bot 75:778–784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2009.06.014
Govindaraj M, Vetriventhan M, Srinivasan M (2015) Importance of genetic diversity assessment in crop plants and its recent advances: an overview of its analytical perspectives. Genet Res Int 2015:431487. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/431487
Hong JH, Kwon YS, Mishra RK, Kim DH (2015) Construction of EST-SSR databases for effective cultivar identification and their applicability to complement for lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) Distinctness. Test Am J Plant Sci 06:113–125. https://doi.org/10.4236/ajps.2015.61013
Ibarra-Torres P, Valadez-Moctezuma E, Pérez-Grajales M, Rodríguez-Campos J, Jaramillo-Flores ME (2015) Inter- and intraspecific differentiation of Capsicum annuum and Capsicum pubescens using ISSR and SSR markers. Sci Hortic 181:137–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2014.10.054
Jaradat NA, Zaid AN, Hussein F (2016) Investigation of the antiobesity and antioxidant properties of wild Plumbago europaea and Plumbago auriculata from North Palestine. Chem Biol Technol Agric 3:31. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40538-016-0082-4
Kishi-Kaboshi M, Aida R, Sasaki K (2018) Genome engineering in ornamental plants: current status and future prospects. Plant Physiol Biochem 131:47–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2018.03.015
Lakshmanan G, Bupesh G, Vignesh A, Sathiyaseelan A, Murugesan K (2016) Micropropagation and anticancer activity of methanolic extract of Plumbago auriculata Lam. Int J Adv Biotech Res 7:2001–2011. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/312197033
Lee ON, Park HY (2017) Assessment of genetic diversity in cultivated radishes (Raphanus sativus ) by agronomic traits and SSR markers. Sci Hortic 223:19–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2017.05.025
Li G, Quiros CF (2001) Sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP), a new marker system based on a simple PCR reaction: its application to mapping and gene tagging in Brassica. Theor Appl Genet 103:455–461. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220100570
Li M, Zhao Z, Miao XJ (2014) Genetic diversity and relationships of apricot cultivars in North China revealed by ISSR and SRAP markers. Sci Hortic 173:20–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2014.04.030
Litrico I, Violle C (2015) Diversity in plant breeding: a new conceptual framework. Trends Plant Sci 20:604–613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2015.07.007
Luo XY, Dai SL (2010) Taxonomic analysis of morphological characters of large-flowered chrysanthemum cultivars. J Beijing Forestry Uni 32:135–140. https://doi.org/10.13332/j.1000-1522.2010.03.013
Peakall R, Smouse PE (2010) GENALEX 6: genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research. Mol Ecol Resour 6:288–295. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-8286.2005.01155
Peng L, Ru M, Wang BQ, Wang Y, Li B, Yu J, Liang ZS (2014) Genetic diversity assessment of a germplasm collection of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge. based on morphology, ISSR and SRAP markers. Biochem Syst Ecol 55:84–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bse.2014.01.020
Pluta S, Mądry W, Sieczko L (2012) Phenotypic diversity for agronomic traits in a collection of blackcurrant (Ribes nigrum L.) cultivars evaluated in Poland. Sci Hortic 145:136–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2012.07.036
Rakonjac V, Akšić MF, Nikolić D, Milatović D, Čolić S (2010) Morphological characterization of ‘Oblačinska’ sour cherry by multivariate analysis. Sci Hortic 125:679–684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2010.05.029
Reddy MP, Sarla N, Siddiq EA (2002) Inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR) polymorphism and its application in plant breeding. Euphytica 128:9–17. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020691618797
Rivera A, Monteagudo AB, Igartua E, Taboada A, García-Ulloa A, Pomar F, Riveiro-Leira M, Silvar C (2016) Assessing genetic and phenotypic diversity in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) landraces from North-West Spain. Sci Hortic 203:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2016.03.006
Song ZQ, Li XF, Wang HG, Wang JH (2010) Genetic diversity and population structure of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bge in China revealed by ISSR and SRAP. Genetica 138:241–249. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-009-9416-5
Van de Vijver LM, Lötter AP (1971) The constituents in the roots of Plumbago auriculata Lam. and Plumbago zeylanica L. responsible for antibacterial activity. Planta Med 20:8–13. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0028-1099658
Wang HZ, Feng SG, Lu JJ, Shi NN, Liu JJ (2009) Phylogenetic study and molecular identification of 31 Dendrobium species using inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) markers. Sci Hortic 122:440–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2009.06.005
Xia H, Zhao GH, Zhang LS, Sun XY, Yin SP, Liang DY, Li Y, Zheng M, Zhao XY (2016) Genetic and variation analyses of growth traits of half-sib Larix olgensis families in northeastern China. Euphytica 212:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-016-1765-4
Yanai H, Ichikawa M (2006) Factor Analysis. . Handbook Statistics 26:257–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-7161(06)26009-7
Yazdanpour F, Khadivi A, Etemadi-Khah A (2018) Phenotypic characterization of black raspberry to select the promising genotypes. Sci Hortic 235:95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2018.02.071
Zietkiewicz E, Rafalski A, Labuda D (1994) Genome fingerprinting by simple sequence repeat (SSR)-anchored polymerase chain reaction amplification. Genom 20:176–183. https://doi.org/10.1006/geno.1994.1151
Acknowledgements
Special thanks to Sichuan Gaonong Ecological Science and Technology Co., Ltd and SICHUAN TIANYI ECOLOGICAL GARDEN GROUP CO., LTD and American journal experts-AJE Company for editing the language of the original manuscript.
Funding
National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFD0600105); Sichuan Science and Technology Program (2018JY0211); Sichuan Science and Technology Program (2017N20008); Sichuan Science and Technology Program (2016NYZ20038).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by J. Huang.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Gao, S., Shen, P. et al. Genetic diversity analysis of intraspecific hybridization between Plumbago auriculata and Plumbago auriculata f. alba based on horticultural traits and molecular markers. Acta Physiol Plant 43, 31 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-020-03188-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-020-03188-9