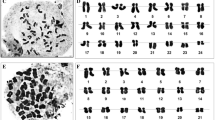
Abstract
Eighteen species and subspecies (34 accessions) of Allium sect. Acanthoprason and 11 species (17 accessions) belonging to other subgenera and sections of Allium were karyologically investigated and include first reports for 12 species. The examined plants of 47 accessions were diploid, three accessions of two species were tetraploid, and in the A. bisotunense accession, we found a mix of di- and triploid individuals. B chromosomes were found in 10 accessions. A basic chromosome number of x = 8 was confirmed for all investigated members of subg. Melanocrommyum and subg. Allium, and x = 9 for Allium tripedale of subg. Nectaroscordum. Idiograms were drawn for each accession, and metaphase images are presented illustrating observed chromosomal variations. Also, karyotype features and asymmetry parameters were calculated for all accessions. Chromosomal aberrations, e.g. aneuploid cells or loss of whole or parts of chromosome arms, were rarely observed. In general, the karyotypes showed low variation in inter- and intrachromosomal asymmetry especially inside of the taxonomic groups, though satellited chromosomes were good markers for subgenera and even specific for two studied sections of subg. Allium. Six different types of satellites were recognized, two of them were newly described: Type P was prevalent in subg. Melanocrommyum, and type O in sect. Codonoprasum. Statistical analyses were performed on five karyological parameters to test correct relationships and also to test previous grouping hypotheses. Although our data confirm distinct karyological characters for the subgenera investigated, the remarkable morphological diversity inside of subg. Melanocrommyum is not mirrored by striking karyological differences.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agapova ND, Arkharova KB, Vakhtina LI, Semskova EA, Tarvis LV (1990) Chisla khromosom tsvetkovykh rastenij flory SSSR. Aceraceae–Menyanthaceae. Nauka, Leningrad (in Russian)
Akhavan A, Saeidi H, Fritsch RM (2014) Allium kuhrangense (Alliaceae) a new species of Allium sect. Acanthoprason Wendelbo from Iran. Phytotaxa 170:213–218
Akhavan A, Saeidi H, Zarre S, Rahiminejad MR (2015) Chromosome numbers and karyotype features of selected species of Allium L. (Amaryllidaceae) sect. Acanthoprason in Iran. Iran J Bot 21:158–164
Araratian AG, Tonian CR (1945) Chromosome numbers in some species of the genus Allium. Herbertia 12: 125. = Araratian AG, Tonian CR (“1945” 1946) Chisla khromosom nekotorykh vidov roda Allium. Dokl Akad Nauk Armyanskoi SSR 2(5):141–143
Aryavand A (1975) Contribution á l’étude cytotaxonomique de quelques angiospermes de l’Iran. Bot Not 128:299–311
Baltisberger M, Hörandl E (2016) Karyotype evolution supports the molecular phylogeny in the genus Ranunculus (Ranunculaceae). Perspect Pl Ecol Evol Syst 18:1–14
Borzatti von Löwenstern A, Garbari F (1999) Reports (1099-1105). In: Kamari G, Felber F, Garbari F (eds) Mediterranean chromosome number reports—9. Fl Medit 9:379–387
Brullo S, Pavone P, Salmeri C (1993) Three new species of Allium (Alliaceae) from Cyprus. Candollea 48:279–290
Brullo S, Guglielmo A, Pavone P, Salmeri C (2007) Cytotaxonomic considerations on Allium stamineum Boiss. group (Alliaceae). Bocconea 21:325–343
Diannelidis T (1951) Cytologische Studien an einigen Allium-Arten aus Nord-Griechenland. Portugaliae Acta Biol Sér A-3:151–170
Escudero M, Martín-Bravo S, Mayrose I, Fernández-Mazuecos M, Fiz-Palacios O et al (2014) Karyotype changes through dysploidy persist longer over evolutionary time than polyploid changes. PLoS ONE 9(1):e85266. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0085266
Fedorov AA (ed) (1974) Chromosome numbers of flowering plants. Original in Russian: translation published by Otto Koeltz Science Publishers, Koenigstein, Germany
Friesen N, Fritsch RM, Blattner FR (2006) Phylogeny and new intrageneric classification of Allium L. (Alliaceae) based on nuclear rDNA ITS sequences. Aliso 22:372–395
Fritsch RM, Abbasi M (2013) A taxonomic review of Allium subg. Melanocrommyum in Iran. IPK Gatersleben, Gatersleben. Available at: http://www.ipk-gatersleben.de/gbisipk-gaterslebendegbis-i/spezialsammlungen/allium-review/
Fritsch RM, Amini Rad M (2013) Allium pseudostrictum (Amaryllidaceae), a new record from Iran. Rostaniha 14:81–84
Fritsch RM, Astanova SB (1998) Uniform karyotypes in different sections of Allium L. subgen. Melanocrommyum (Webb & Berth.) Rouy from Central Asia. Feddes Repert 109:539–549
Fritsch RM, Friesen N (2002) Evolution, domestication, and taxonomy. In: Rabinowitch HD, Currah L (eds) Allium crop science: recent advances. CABI Publishing, Wallingford, pp 5–30
Fritsch RM, Maroofi H (2010) New species and new records of Allium L. (Alliaceae) from Iran. Phyton (Horn) 50:1–26
Fritsch RM, Blattner FR, Gurushidze M (2010) New classification of Allium L. subg. Melanocrommyum (Webb & Berthel.) Rouy (Alliaceae) based on molecular and morphological characters. Phyton (Horn) 49:145–220
Garbari F, Crisman E (1988) Cytotaxonomical contributions to the Jordanian Flora. 1. Webbia 42:21–41
Genc I, Özhatay FN (2014) Allium efeae (Amaryllidaceae), a new species from northwest Anatolia, Turkey. Turkish J Bot 38:1022–1025
Genc I, Özhatay N, Cevri M (2013) A karyomorphological study of the genus Allium (sect. Melanocrommyum) from Turkey. Caryologia 66:31–40
Ghaffari SM (1987) Chromosome studies in some flowering plants of Iran. Rev Cytol Biol Vég Bot 10:3–8
Ghaffari SM (2006a) New or rare chromosome counts of some angiosperm species from Iran. Iran J Bot 11:185–192
Ghaffari SM (2006b) New cytogenetic information on Allium iranicum (Alliaceae) from Iran. Biologia (Bratislava) 61:375–379
Ghahreman A, Attar F (1999) Biodiversity of plant species in Iran, vol I. Central Herbarium of Tehran University, Tehran
Goldblatt P (1974) Chromosome numbers of phanerogams. 5. Ann Missouri Bot Gard 61:901–903
Goldblatt P (ed) (1981, 1984, 1985, 1988) Index to plant chromosome numbers for 1975–1978 (pp 553), 1979–1981 (pp 427), 1982–1983 (pp 224), 1984–1985 (pp 264). Missouri Botanical Garden, St. Louis
Goldblatt P, Johnson DE (eds) (1990, 1991, 1994, 1996, 1999, 2000, 2003) Index to plant chromosome numbers for 1986–1987 (pp 243), 1988–1989 (pp 238), 1990–1991 (pp 267), 1992–1993 (pp 276), 1994–1995 (pp 208), 1996–1997 (pp 188), 1998–2000 (pp 297). Missouri Botanical Garden, St. Louis
Govaerts R, Kington S, Friesen N, Fritsch R, Snijman DA, Marcucci R, Silverstone-Sopkin PA, Brullo S (2017) World checklist of Amaryllidaceae. Available at: http://apps.kew.org/wcsp/. Accessed 25 Jan 2017
Gower JC (1971) A general coefficient of similarity and some of its properties. Biometrics 27:857–871. https://doi.org/10.2307/2528823
Gurushidze M, Blattner FR (2013) Phylogenetic tree calculated with Bayesian phylogenetic inference from ITS sequences. In: Fritsch RM, Abbasi M (eds) A taxonomic review of Allium subg. Melanocrommyum in Iran. IPK Gatersleben, Gatersleben, pp 199–202
Gurushidze M, Fritsch RM, Blattner FR (2008) Phylogenetic analysis of Allium subg. Melanocrommyum infers cryptic species and demands a new sectional classification. Molec Phylogen Evol 49:997–1007
Gurushidze M, Fritsch RM, Blattner FR (2010) Species level phylogeny of Allium subgenus Melanocrommyum: incomplete lineage sorting, intraspecific polymorphism, hybridization and trnF gene duplication. Taxon 59:829–840
Gurushidze M, Fuchs J, Blattner FR (2012) The evolution of genome size variation in drumstick onions (Allium subgenus Melanocrommyum). Syst Bot 37:96–104
Hammer Ø, Harper DAT, Ryan PD (2001) PAST: paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol Electronica 4:1–9
Harpke D, Meng S, Rutten T, Kerndorff H, Blattner FR (2013) Phylogeny of Crocus (Iridaceae) based on one chloroplast and two nuclear loci: ancient hybridization and chromosome number evolution. Mol Phylogen Evol 66:617–627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2012.10.007
Hosseini S, Go R (2010) Cytogenetic study of some Allium species (subgenus Allium and Melanocrommyum) in Iran. Cytologia 75:99–108
Jakob SS, Blattner FR (2006) A chloroplast genealogy of Hordeum (Poaceae): long-term persisting haplotypes, incomplete lineage sorting, regional extinction, and the consequences for phylogenetic inference. Molec Biol Evol 23:1602–1612
Johnson MAT (1982) Karyotypes of some Greek species of Allium (Alliaceae). Ann Mus Goulandris 5:107–119
Johnson MAT, Brandham PE (1997) New chromosome numbers in petaloid monocotyledons and in other miscellaneous angiosperms. Kew Bull 52:121–138
Johnson MAT, Özhatay N (1996) Cytology of Allium sect. Allium. In: Mathew B (ed) A review of Allium sect. Allium. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, pp 17–40
Karavokyrou E, Tzanoudakis D (1991) The genus Allium in Greece: II. A cytogeographical study of the E Aegean species. Bot Chron (Patras) 10:777–784
Kollmann F (1969) Cytotaxonomic polymorphism in the Allium erdelii. Israel J Bot 18:61–75
Kollmann F (1970) New chromosome counts in Allium species of Palestine and Mount Hermon. Israel J Bot 19:245–248
Kollmann F, von Bothmer R (1989) Allium affine Ledeb., taxonomy and karyotype. Israel J Bot 38:47–57
Koyuncu M, Özhatay N (1983) Güney Anadolu’num Bazi Allium Türleri (Sect. Melanocrommyum) Üzerinde Sitotaksonimik Arastirmalar. Ankara Üniv Eczacilik Fak Mecmuasi 13:159–169
Levan A (1932) Cytological studies in Allium II: chromosome morphological contribution. Hereditas (Lund) 16:257–294
Levan A (1935) Cytological studies in Allium. VI. The chromosome morphology of some diploid species of Allium. Hereditas (Lund) 20:289–330
Levan A, Fredga K, Sandberg AA (1964) Nomenclature for centromeric position on chromosomes. Hereditas (Lund) 52:201–220
Miryeganeh M, Movafeghi A (2011) Karyotype analysis in some species of Allium section Allium (Alliaceae). Roman J Biol Pl Biol 56:17–27
Moore RJ (ed) (1973) Index to plant chromosome numbers for 1967–1971. Regnum Veg 90: 1–539
Moore RJ (ed) (1977) Index to plant chromosome numbers for 1973/1974. Regnum Veg 96: 1–257
Moore DM (1982) Flora Europaea check-list and chromosome index. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Oganesian ME, Agababian MV (2001) Sem. 3 Alliaceae, Lukovye. In: Takhtajan AL (ed) Flora Armenii. Tom 10. Gantner, Ruggell, pp 280–348
Ornduff R (ed) (1967) Index to plant chromosome numbers for 1965. Regnum Veg 50: 1–128
Ornduff R (ed) (1968) Index to plant chromosome numbers for 1966. Regnum Veg 55: 1–126
Özhatay N (1984) Cytotaxonomic studies on the genus Allium in European Turkey and around Istanbul II. Sect. Codonoprasum. J Fac Pharm Istanbul 20:29–42
Özhatay N (1986) Allium species in North Anatolia and their chromosome numbers. Doga Türk Biol Derg 10:452–458 (in Turkish)
Özhatay N (1993) Allium in Turkey: distribution, diversity, endemism and chromosome number. In: Demiriz H, Özhatay N (eds) OPTIMA: proceedings of the 5th OPTIMA meeting Istanbul, 8–15 Sept. 1986. OPTIMA, Istanbul, pp 247–271
Özhatay N, Johnson MAT (1996) Some karyological remarks on Turkish Allium sect. Allium, Bellevalia, Muscari, and Ornithogalum subgen. Ornithogalum. Bocconea 5:239–249
Ozturk M, Gucel S, Altay V, Altundag E (2012) Alliums, an underutilized genetic resource in the East Mediterranean. Acta Hort 969:303–309
Pastor J (1982) Karyology of Allium species from the Iberian Peninsula. Phyton (Horn) 22:171–200
Pedersen K, Wendelbo P (1966) Chromosome numbers of some SW Asian Allium species. Blyttia 24:307–313
Persson K, Wendelbo P (1979) The taxonomic position of Nectaroscordum koelzii (Liliaceae). Bot Not 132:191–196
Peruzzi L, Altinordu F (2014) A proposal for a multivariate quantitative approach to infer karyological relationships among taxa. Comparative Cytogenet 8:337–349. https://doi.org/10.3897/CompCytogen.v8i4.8564
Peruzzi L, Carta A, Altınordu F (2017) Chromosome diversity and evolution in Allium (Amaryllidaceae, Allioideae). Pl Biosystems 151:212–220. https://doi.org/10.1080/11263504.2016.1149123
Pogosian AI (1974) Chisla khromosom nekotorykh vidov tsvetkovykh rastenij flory gornogo massiva Aragats. Tsitol Genet 8:449–451
Pogosian AI (1981) Analiz morfologicheskikh parametrov khromosom nekotorykh Kavkazskikh vidov roda Allium L. Fl Rastitel’nost’ Rastitel’nye Resursy Armyansk SSR 7:39–58
Pogosian AI (1983) Chromosome numbers of some species of the genus Allium (Alliaceae) distributed in Armenia and Iran. Bot Zhurn (Moscow & Leningrad) 68:652–660 (in Russian)
Pogosian AI (1985a) Citotaksonomicheskoe issledovanie nekotorykh vidov roda Allium L. iz sektsii Acanthoprason Wendelbo (Alliaceae). Sborn Nauch Trudov Armyansk Otd Vsesoyuzn Bot Obshch 9:82–103
Pogosian AI (1985b) Cytotaxonomic study in Allium derderianum (Alliaceae). Bot Zhurn (Moscow & Leningrad) 70:356–361 (in Russian)
Pogosian AI (1988a) Citotaksonomicheskoe issledovanie Allium dictyoprasum C. A. Mey. i A. viride Grossh. (Alliaceae). Flora Rastitel’nost’ Rastitel’nye Resursy Armyansk SSR 11:51–63
Pogosian AI (1988b) Cytotaxonomic study of Allium affine and Allium transcaucasicum (Alliaceae). Bot Zhurn (Moscow & Leningrad) 73:669–674 (in Russian)
Pogosian AI (1991) Citotaksonomicheskoe issledovanie Kavkazskikh lukov podroda Allium (Alliaceae). Flora Rastitel’nost’ Rastitel’nye Resursy Armenii 13:135–153
Pogosian AI (1997) Chisla khromosom nekotorykh vidov odnodol’nykh iz Zakavkaz’ia. Bot Zhurn (St. Petersburg) 82(6):117–118
Pogosian AI, Narinian SG, Voskanian VE (1969) K kariogeograficheskomy izucheniiu flory gornogo massiva Aragats. Biol Zhurn Armenii 22(10):12–19
Schubert I (2007) Chromosome evolution. Curr Opin Pl Biol 10:109–115
Tahbaz F (1971) The Allium “Taree irani” of the group Ampeloprasum L. cultivated in Iran, in the area of Tehran. Bull Soc Bot France 118:753–761
Tahbaz F (1976) Comparative study of the caryotypes of two Allium taxa of the Ampeloprasum group cultivated in Iran. Compt Rend Hebd Seances Acad Sci D 283:1185–1188
Tanker N, Kurucu S (1979) Cytotaxonomical researches on some species of Allium naturally growing in Turkey. J Fac Pharm Ankara 9:64–80 (in Turkish)
Tzanoudakis D (1983) Karyotypes of ten taxa of Allium section Scorodon from Greece. Caryologia 36:259–284
Tzanoudakis D (1986) Karyotype variation in Allium sect. Molium G. Don from Greece. Caryologia 39:69–88
Tzanoudakis D (1992) Karyotype variation and evolution in the Greek Allium. In: Hanelt P, Hammer K, Knüpffer H (eds) The genus Allium—taxonomic problems and genetic resources. Institut für Genetik und Kulturpflanzenforschung, Gatersleben, pp 305–320
Tzanoudakis D (1999) The genus Allium in Cyprus: a preliminary cytotaxonomical study. Bocconea 11:105–115
Vakhtina LI (1969) Sravnitel’no-kariologicheskoe issledovanie nekotorykh vidov luka sekcii Molium Don. Bot Zhurn (Moscow & Leningrad) 54:143–150
Vakhtina LI (1985) Chromosome numbers in some species of the genus Allium (Alliaceae) in the flora of the USSR. Bot Zhurn (Moscow & Leningrad) 70:700–701 (in Russian)
Vakhtina LI, Kudryashova GL (1985) Karyosystematic study in some species of the section Codonoprasum of the genus Allium (Alliaceae). Bot Zhurn (Moscow & Leningrad) 70:76–88 (in Russian)
Ved Brat S (1965) Genetic system in Allium. 1. Chromosome variation. Chromosoma 16:486–499
Vosa CG (1976) Heterochromatic banding patterns in Allium. II. Heterochromatin variation in species of the paniculatum group. Chromosoma 57:119–133
Vosa CG (1977) Heterochromatin patterns and species relationships. Nucleus (Calcutta) 20:33–41
Wendelbo P (1971) Alliaceae. In: Rechinger KH (ed) Flora Iranica. Flora des iranischen Hochlandes und der umrahmenden Gebirge, Persien, Afghanistan, Teile von Westpakistan, Nordiraq, Azerbaidjan, Turkmenistan. No. 76. Akademische Druck- und Verlagsanstalt, Graz
Wetschnig W (1992) Chromosomenzahlen Kärntner Gefäßpflanzen (Teil 3): Karyologie und Verbreitung der Allium-Arten (Alliaceae) in Kärnten. Carinthia II 182:497–533
Zakirova RO, Vakhtina LI (1974) A cytophotometric and caryological study of some Allium species of the subgenus Melanocrommyum (Webb et Berth.) Wendelbo, section Melanocrommyum. Bot Zhurn (Moscow & Leningrad) 59:1819–1827 (in Russian)
Acknowledgements
This paper presents data from the first author’s (A. D.) PhD thesis fulfilled at Iranian biological resources center (IBRC). This organization is gratefully acknowledged for financial support. We would like to express our special thanks to Dr. H. Moazzeni and Mr. H. Ramezani for their valuable help during collecting missions. The latter mentioned person is also thanked for valuable guidance how to cultivate and root bulbs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling editor: Hanna Schneeweiss.
Information on Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material. These tables include mean and standard deviation of short and long chromosome arms, satellite fragments and centromeric indices of all studied accessions. All idiograms are based on these data.
Online Resource 1a–e.
Arm lengths [in µm] with standard deviations (in the vertical sequence of satellites, short arms, long arms and centromere indices) in diploid members of sect. Acanthoprason (PDF 944 kb)
Online Resource 2.
Arm lengths [in µm] with standard deviations (in the vertical sequence of satellites, short arms, long arms and centromere indices) in members of sect. Acanthoprason and sect. Melanocrommyum with more than 20 chromosomes (PDF 390 kb)
Online Resource 3.
Arm lengths [in µm] with standard deviations (in the vertical sequence of satellites, short arms, long arms and centromere indices) in diploid members of other sections of subg. Melanocrommyum and in A. tripedale, subg. Nectaroscordum (PDF 438 kb)
Online Resource 4.
Arm lengths [in µm] with standard deviations (in the vertical sequence of satellites, short arms, long arms and centromere indices) in diploid members of subg. Allium sect. Allium (PDF 425 kb)
Online Resource 5.
Arm lengths [in µm] with standard deviations (in the vertical sequence of satellites, short arms, long arms and centromere indices) in A. pseudoampeloprasum, sect. Allium (PDF 310 kb)
Online Resource 6.
Arm lengths [in µm] with standard deviations (in the vertical sequence of satellites, short arms, long arms and centromere indices) in A. stamineum, sect. Codonoprasum (PDF 361 kb)
Information on Electronic Supplementary Material
Information on Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material. These tables include mean and standard deviation of short and long chromosome arms, satellite fragments and centromeric indices of all studied accessions. All idiograms are based on these data.
Online Resource 1a–e. Arm lengths [in µm] with standard deviations (in the vertical sequence of satellites, short arms, long arms and centromere indices) in diploid members of sect. Acanthoprason.
Online Resource 2. Arm lengths [in µm] with standard deviations (in the vertical sequence of satellites, short arms, long arms and centromere indices) in members of sect. Acanthoprason and sect. Melanocrommyum with more than 20 chromosomes.
Online Resource 3. Arm lengths [in µm] with standard deviations (in the vertical sequence of satellites, short arms, long arms and centromere indices) in diploid members of other sections of subg. Melanocrommyum and in A. tripedale, subg. Nectaroscordum.
Online Resource 4. Arm lengths [in µm] with standard deviations (in the vertical sequence of satellites, short arms, long arms and centromere indices) in diploid members of subg. Allium sect. Allium.
Online Resource 5. Arm lengths [in µm] with standard deviations (in the vertical sequence of satellites, short arms, long arms and centromere indices) in A. pseudoampeloprasum, sect. Allium.
Online Resource 6. Arm lengths [in µm] with standard deviations (in the vertical sequence of satellites, short arms, long arms and centromere indices) in A. stamineum, sect. Codonoprasum.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dolatyari, A., Saeidi Mehrvarz, S., Shahzadeh Fazeli, S.A. et al. Karyological studies of Iranian Allium L. (Amaryllidaceae) species with focus on sect. Acanthoprason. 1. Mitotic chromosomes. Plant Syst Evol 304, 583–606 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-017-1489-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-017-1489-5