Archaeologists digging at the northern end of Trafalgar Square found evidence that Saxon London’s center was bigger and extended further west long ago than previously believed.
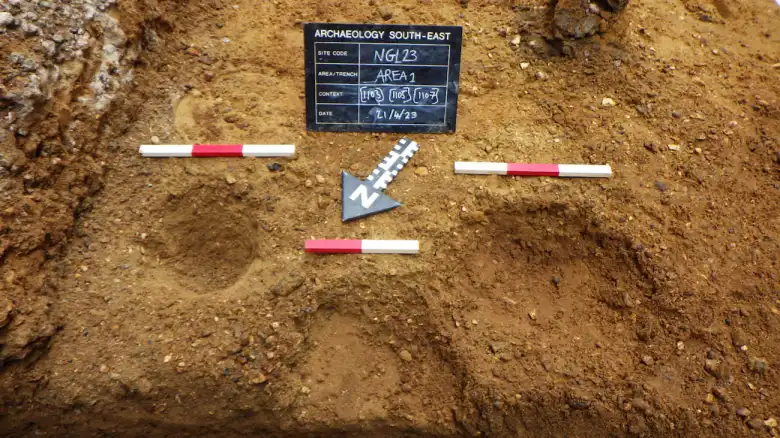
A Saxon town known as Lundenwic once stood where London’s National Gallery now stands, say experts who have found evidence including a hearth from the 7th or 8th century.
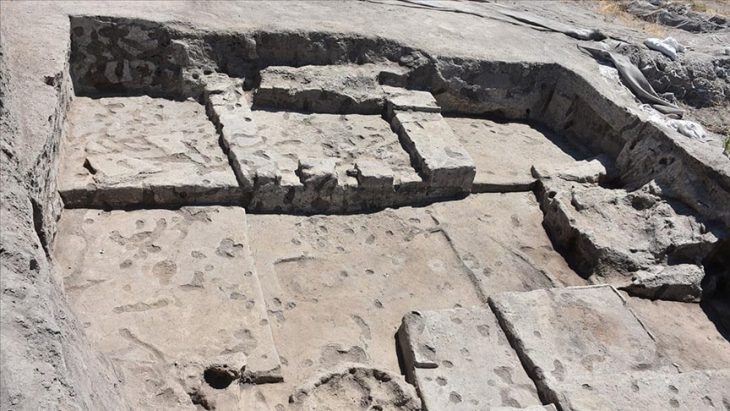
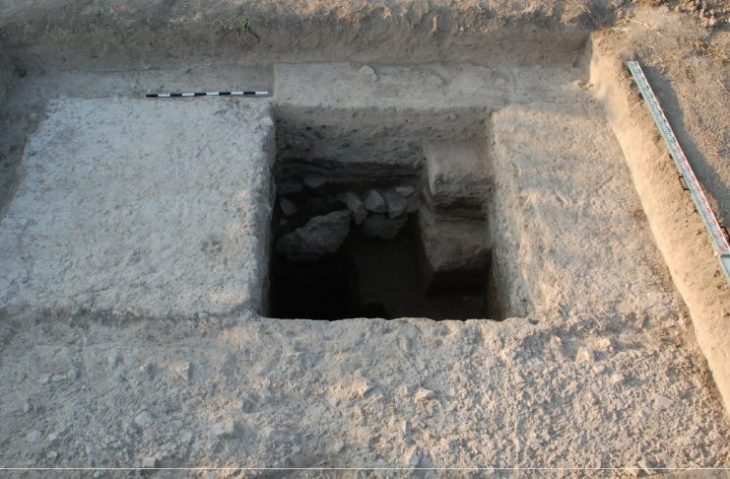
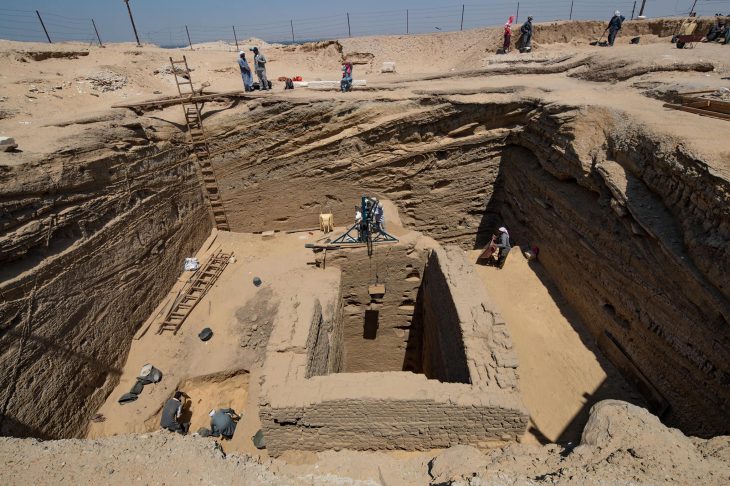
A report from excavations of Jubilee Walk, part of the National Gallery at the north end of Trafalgar Square, was released by archaeologists from Archaeology South-East, part of the UCL Institute of Archaeology. The findings detail how the urban center of Saxon London extended further west than previously believed.
The archaeological activity was prompted by the need to build a tunnel connecting the Gallery’s Sainsbury Wing and the Wilkins Building, as well as improvements to the public realm adjacent to Jubilee Walk. This pathway, built during the 1991 Sainsbury Wing construction, has historical significance dating back to the reign of King Richard II, serving a variety of purposes ranging from Royal Mews to residential housing.
The excavations were undertaken as part of the National Gallery’s ‘NG200: Welcome’, a redevelopment project forming part of the Gallery’s Bicentenary celebrations.
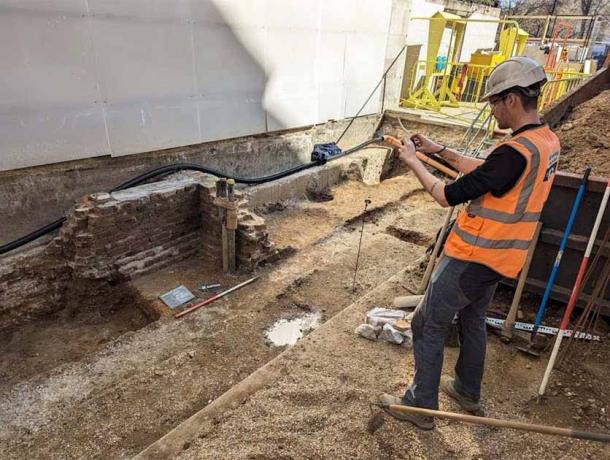

“The evidence we uncovered suggests the urban centre of Lundenwic extends further west than originally thought. This was made all the more exciting by having the chance to share that information, and how it relates to archaeology across London, with young people from this city” says Stephen White, senior archaeologist with Archaeology South-East.
The walled Roman city of Londinium was abandoned by its inhabitants in the fifth century CE. With the arrival of the Saxons, the settlement shifted west along the modern Strand. By the seventh century, it was referred to as Lundenwic and functioned mainly as a waterfront trading hub. The National Gallery is located at the western end of this settlement; while excavations in the surrounding area have previously yielded Saxon material, this is the first excavation to show that the urban center extended this far west.
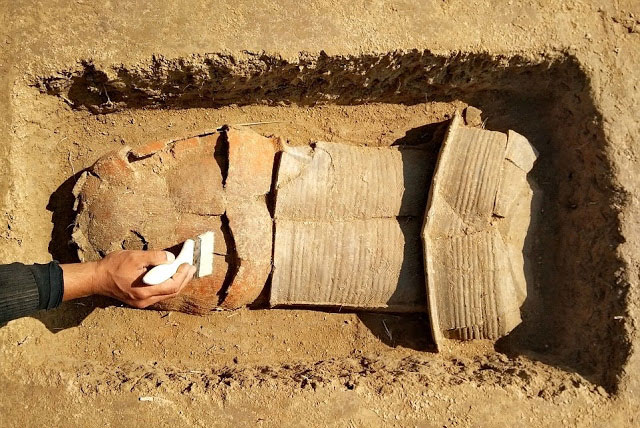
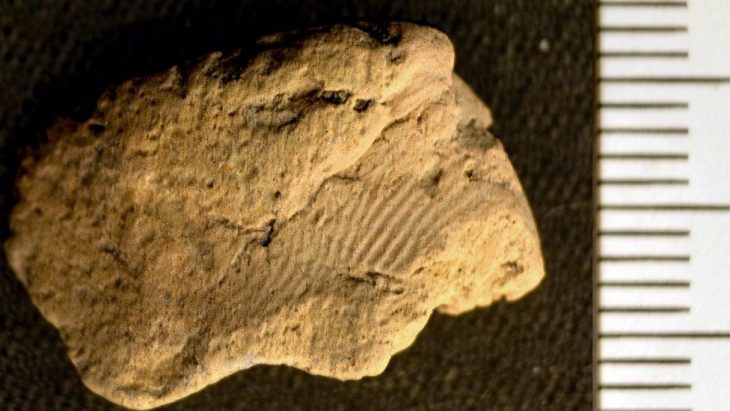
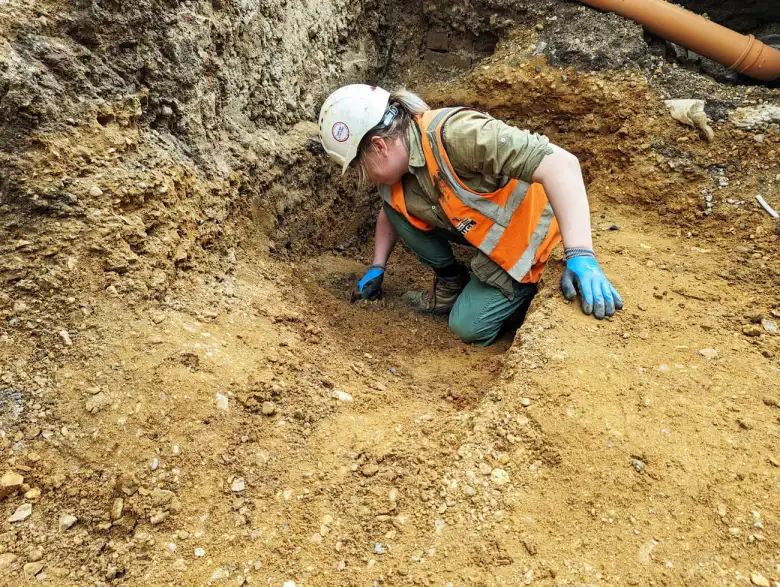
Archaeologists unearthed a hearth, postholes, stakeholes, pits, ditches, and leveling deposits, which initial interpretations suggest represent the reworking of fence lines and evolving property boundaries in this western suburb of Lundenwic.
The hearth was radiocarbon-dated and revealed a date range between 659-774 AD for the earliest occupation. Above this sequence of Saxon layers were post-medieval walls. The team noticed the walls were fixed up and changed over the following centuries as the area transformed.

The Roman city of Londinium fell into a long, slow decline beginning in the third century AD and was eventually abandoned. The new Saxon settlers saw no need for a walled city. They eventually established a new town, Lundenwic, outside the city walls. Lundunwic grew to be the area’s main port and trading hub, with ‘wic’ meaning Saxon for trading place.
The National Gallery is one of the world’s greatest art galleries. Founded by Parliament in 1824, the Gallery houses the nation’s collection of paintings in the Western European tradition from the late 13th to the early 20th century.
When archaeological research opens up previously undiscovered scenes and new chapters in the history of cities like London, it’s always exciting. New hints regarding the evolution of the metropolis beneath its current streets were discovered by this project.
Cover Photo: © Archaeology South-East/UCL