EP0103791A2 - Coding method for an electronic key - Google Patents
Coding method for an electronic key Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0103791A2 EP0103791A2 EP83108591A EP83108591A EP0103791A2 EP 0103791 A2 EP0103791 A2 EP 0103791A2 EP 83108591 A EP83108591 A EP 83108591A EP 83108591 A EP83108591 A EP 83108591A EP 0103791 A2 EP0103791 A2 EP 0103791A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- receiver
- transmitter
- code
- signal
- electronic key
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G07—CHECKING-DEVICES
- G07C—TIME OR ATTENDANCE REGISTERS; REGISTERING OR INDICATING THE WORKING OF MACHINES; GENERATING RANDOM NUMBERS; VOTING OR LOTTERY APPARATUS; ARRANGEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS FOR CHECKING NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- G07C9/00—Individual registration on entry or exit
- G07C9/00174—Electronically operated locks; Circuits therefor; Nonmechanical keys therefor, e.g. passive or active electrical keys or other data carriers without mechanical keys
- G07C9/00182—Electronically operated locks; Circuits therefor; Nonmechanical keys therefor, e.g. passive or active electrical keys or other data carriers without mechanical keys operated with unidirectional data transmission between data carrier and locks
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G07—CHECKING-DEVICES
- G07C—TIME OR ATTENDANCE REGISTERS; REGISTERING OR INDICATING THE WORKING OF MACHINES; GENERATING RANDOM NUMBERS; VOTING OR LOTTERY APPARATUS; ARRANGEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS FOR CHECKING NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- G07C9/00—Individual registration on entry or exit
- G07C9/20—Individual registration on entry or exit involving the use of a pass
- G07C9/21—Individual registration on entry or exit involving the use of a pass having a variable access code
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G07—CHECKING-DEVICES
- G07C—TIME OR ATTENDANCE REGISTERS; REGISTERING OR INDICATING THE WORKING OF MACHINES; GENERATING RANDOM NUMBERS; VOTING OR LOTTERY APPARATUS; ARRANGEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS FOR CHECKING NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- G07C9/00—Individual registration on entry or exit
- G07C9/00174—Electronically operated locks; Circuits therefor; Nonmechanical keys therefor, e.g. passive or active electrical keys or other data carriers without mechanical keys
- G07C9/00182—Electronically operated locks; Circuits therefor; Nonmechanical keys therefor, e.g. passive or active electrical keys or other data carriers without mechanical keys operated with unidirectional data transmission between data carrier and locks
- G07C2009/00238—Electronically operated locks; Circuits therefor; Nonmechanical keys therefor, e.g. passive or active electrical keys or other data carriers without mechanical keys operated with unidirectional data transmission between data carrier and locks the transmittted data signal containing a code which is changed
- G07C2009/00253—Electronically operated locks; Circuits therefor; Nonmechanical keys therefor, e.g. passive or active electrical keys or other data carriers without mechanical keys operated with unidirectional data transmission between data carrier and locks the transmittted data signal containing a code which is changed dynamically, e.g. variable code - rolling code
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G07—CHECKING-DEVICES
- G07C—TIME OR ATTENDANCE REGISTERS; REGISTERING OR INDICATING THE WORKING OF MACHINES; GENERATING RANDOM NUMBERS; VOTING OR LOTTERY APPARATUS; ARRANGEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS FOR CHECKING NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- G07C9/00—Individual registration on entry or exit
- G07C9/00174—Electronically operated locks; Circuits therefor; Nonmechanical keys therefor, e.g. passive or active electrical keys or other data carriers without mechanical keys
- G07C2009/00753—Electronically operated locks; Circuits therefor; Nonmechanical keys therefor, e.g. passive or active electrical keys or other data carriers without mechanical keys operated by active electrical keys
- G07C2009/00769—Electronically operated locks; Circuits therefor; Nonmechanical keys therefor, e.g. passive or active electrical keys or other data carriers without mechanical keys operated by active electrical keys with data transmission performed by wireless means
- G07C2009/00785—Electronically operated locks; Circuits therefor; Nonmechanical keys therefor, e.g. passive or active electrical keys or other data carriers without mechanical keys operated by active electrical keys with data transmission performed by wireless means by light
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G07—CHECKING-DEVICES
- G07C—TIME OR ATTENDANCE REGISTERS; REGISTERING OR INDICATING THE WORKING OF MACHINES; GENERATING RANDOM NUMBERS; VOTING OR LOTTERY APPARATUS; ARRANGEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS FOR CHECKING NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- G07C2209/00—Indexing scheme relating to groups G07C9/00 - G07C9/38
- G07C2209/06—Involving synchronization or resynchronization between transmitter and receiver; reordering of codes
Definitions
- the invention relates to a method for code security in an electronic key, in particular for motor vehicles with a built-in central locking system, which consists of a transmitter which emits a coded infrared signal which is received by a receiver tuned to the code, the code of Signal at the transmitter and receiver is adjustable.
- the copying option described can only be prevented if the transmitter and receiver are brought so close together that a second receiver is not in the beam area of the transmitter. However, this is practically not possible in motor vehicles since the receiver is arranged inside the vehicle while the transmitter is outside the vehicle. Due to reflections, for example on the panes, there is a risk that the emitted signal, even when approaching closely, is scattered and can be illegally picked up by a second recipient.
- An electronic key of the type mentioned is known from DE-A-29 06 665.
- the known key has switch groups for adjusting the code on the transmitter and receiver, as a result of which the code can be set by the user.
- the object of the invention is to provide a method for code security for an electronic key, which ensures in a simple manner that the electronic key cannot be used by unauthorized persons.
- this object is achieved according to the invention by using a random generator which selects an arbitrary bit pattern from the number of code possibilities and transmits the transmitter and receiver, preferably by means of a forced synchronization.
- Illegal use of a copied code is practically excluded.
- the Exchange of information of the valid code by means of a forced synchronization, which is achieved, for example, by electronically connecting the transmitter and receiver. This is done, for example, by plugging the transmitter and receiver together in the vehicle so that other functions, for example switching on the ignition, are guaranteed.
- a forced synchronization which is achieved, for example, by electronically connecting the transmitter and receiver. This is done, for example, by plugging the transmitter and receiver together in the vehicle so that other functions, for example switching on the ignition, are guaranteed.
- the transmitter sends a reset code after a battery change, which ensures that the electronic lock can be opened in any case.
- a further embodiment provides that when the operating voltage of the receiver drops below a certain value by means of a latch circuit e.g. Relay, a bolt is operated, which enables unlocking with a mechanical key.
- a latch circuit e.g. Relay
- the reset code can also be started, as when changing the battery in the transmitter, or the next-valid code of the random number generator can be transmitted to the receiver or to the transmitter by means of forced synchronization.
- Another embodiment of the method according to the invention is that different to one receiver belonging transmitter receive an identifier, and that the code valid for each transmitter is stored in the receiver. This has the advantage that, for example, several keys can be issued for a vehicle and at the same time the advantages of coding with the random number generator are retained for each individual key.
- the method according to the invention preferably works.
- the transmitter can either be equipped with an operating button which alternately operates the functions "open” and "closed”.
- two different buttons can also be arranged on the transmitter for this purpose.
- the reset code can be sent, for example, by pressing one of the buttons for a long time.
- Another advantage of the method according to the invention is, for example, that when the vehicle is handed over to the workshop, the lock is opened electronically and can be operated with the mechanical key, so. that the electronic key remains in the user's hand.
- both the transmitter and the receiver are provided with an automatic switching system which cyclically interchange the code, if by any mistake the forced synchronization has not been performed. This ensures that copying the code is of no use even if, for example, only the vehicle is opened without starting it, so that forced synchronization has not taken place. In this case there would otherwise be the possibility that illegal use could take place by means of a copied signal.
- the identification of each transmitter from the multitude of transmitter / receiver combinations can be carried out in the manner of a selection switch, which is described, for example, in DE-U-80 05 555.
- the selection switch can consist of a stamp that cuts through the corresponding coding inputs. In this way, a characteristic image pattern is generated which is read upon initialization in order to have the program start at the key-specific point for the code.
- the identification code is expediently a reset or "door to" code at the same time. This means that a clear assignment is also possible when reordering keys; when the key is potted, it is electronic by sending the signal, e.g. "Door closed" to determine.
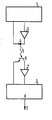
- transmitter 1 denotes a transmitter and 2 the associated receiver.
- transmitter 1 and receiver 2 each consist of a CMOS microprocessor with subsequent amplifier 3 or 7 and infrared transmitter diode 4 or phototransistor 6.
- Transmitter 1 sends out the coded infrared signal 5 via the photodiode 4, which is received by the fctotransistor 6 and via the Amplifier 7 is fed to the receiver 2.
- a control signal 9 appears, with which the central locking of the motor vehicle is operated.
- the random generator required for the method according to the invention can be easily implemented with the help of the microprocessors already present and can be accommodated either in the transmitter 1 or in the receiver 2.
Abstract
Description
Die Erfindung betrifft ein Verfahren zur Code-Sicherung bei einem elektronischen Schlüssel, insbesondere für Kraftfahrzeuge mit eingebauter Zentralverriegelung, der aus einem Sender besteht, welcher ein codiertes Infrarot- Signal aussendet, das von einem auf den Code abgestimmten Empfänger aufgenommen wird, wobei der Code des Signals bei Sender und Empfänger verstellbar ist.The invention relates to a method for code security in an electronic key, in particular for motor vehicles with a built-in central locking system, which consists of a transmitter which emits a coded infrared signal which is received by a receiver tuned to the code, the code of Signal at the transmitter and receiver is adjustable.
Bei derartigen Systemen, die auf der Codierung eines Signals auf der Senderseite und der Entschlüsselung dieses Signals auf der Empfängerseite beruhen, beseht die Gefahr, daß von jedem beliebigen Empfänger das codierte Signal aufgenommen und gespeichert-werden kann, wenn sich dieser während des Sendevorganges im Strahlbereich des Senders befindet. So läßt sich verhältnismäßig einfach eine Kopie des elektronischen Schlüssels herstellen, wodurch eine unbefugte Benutzung eines Kraftfahrzeuges ermöglicht wird.In such systems, which are based on the coding of a signal on the transmitter side and the decryption of this signal on the receiver side, there is a risk that the coded signal can be picked up and stored by any receiver if it is in the beam area during the transmission process of the transmitter. It is relatively easy to make a copy of the electronic key, which enables unauthorized use of a motor vehicle.
Die beschriebene Kopiermöglichkeit läßt sich nur verhindern, wenn Sender und Empfänger so nahe zusammengebracht werden, daß ein zweiter Empfänger nicht im Strahlbereich des Senders liegt. Dies ist aber bei Kraftfahrzeugen praktisch nicht möglich, da der Empfänger im Inneren des Fahrzeugs angeordnet ist, während sich der Sender außerhalb des Fahrzeugs befindet. Durch Reflexionen, beispielsweise an_den Scheiben, ist somit die Gefahr gegeben, daß das ausgesendete Signal, selbst bei nahem Herangehen, gestreut wird und von einem zweiten Empfänger unrechtmäßig aufgenommen werden kann.The copying option described can only be prevented if the transmitter and receiver are brought so close together that a second receiver is not in the beam area of the transmitter. However, this is practically not possible in motor vehicles since the receiver is arranged inside the vehicle while the transmitter is outside the vehicle. Due to reflections, for example on the panes, there is a risk that the emitted signal, even when approaching closely, is scattered and can be illegally picked up by a second recipient.
Ein elektronischer Schlüssel der eingangs genannten Art ist aus der DE-A-29 06 665 bekannt. Der bekannte Schlüssel besitzt zum Verstellen des Codes an Sender und Empfänger Schaltergruppen, wodurch der Code durch den Benutzer einstellbar ist. Es ist hiermit im Prinzip zwar möglich, daß der Benutzer nach jedem Aufschließen einen neuen Code am Gerät einstellt, jedoch besteht einerseits die Gefahr, daß der Code an Sender und Empfänger unterschiedlich eingestellt wird, wodurch sich das Fahrzeug nicht mehr öffnen läßt und andererseits widerspricht es der bequemen Handhabung derartiger elektronischer Schlösser, so daß im allgemeinen ein neuer Code nur bei Besitzerwechsel des Fahrzeugs eingestellt wird.An electronic key of the type mentioned is known from DE-A-29 06 665. The known key has switch groups for adjusting the code on the transmitter and receiver, as a result of which the code can be set by the user. In principle, it is hereby possible for the user to set a new code on the device after each unlocking, but on the one hand there is the risk that the code on the transmitter and receiver is set differently, as a result of which the vehicle can no longer be opened and on the other hand it contradicts the convenient handling of such electronic locks, so that a new code is generally only set when the vehicle changes hands.
Aufgabe der Erfindung ist es, ein Verfahren zur Code-Sicherung bei einem elektronischen Schlüssel anzugeben, das in einfacher Weise gewährleistet, daß der elektronische Schlüssel nicht durch unbefugte Personen benutzt werden kann.The object of the invention is to provide a method for code security for an electronic key, which ensures in a simple manner that the electronic key cannot be used by unauthorized persons.
Diese Aufgabe wird bei dem eingangs genannten Verfahren erfindungsgemäß durch die Verwendung eines Zufallsgenerators gelöst, der aus der Anzahl der Code-Möglichkeiten ein beliebiges Bit-Muster auswählt und Sender und Empfänger, vorzugsweise durch eine Zwangssynchronisation, übermittelt.In the method mentioned at the outset, this object is achieved according to the invention by using a random generator which selects an arbitrary bit pattern from the number of code possibilities and transmits the transmitter and receiver, preferably by means of a forced synchronization.
Hiermit wird der Vorteil erzielt, daß aus der großen Anzahl von Möglichkeiten, bei beispielsweise 24 Bits 2 = 16 Millionen, ein beliebiges Bildmuster ausgewählt wird. Ein unrechtmäßiger Gebrauch eines kopierten Code ist damit praktisch.ausgeschlossen. Vorzugsweise erfolgt der Informationsaustausch des gültigen Code mittels einer Zwangssynchronisation, die beispielsweise dadurch erreicht wird, daß Sender und Empfänger elektronische miteinander verbunden werden. Dies geschieht beispielsweise dadurch, daß Sender und Empfänger im Fahrzeug zusammengesteckt werden, damit andere Funktionen, beispielsweise Einschalten der Zündung, gewährleistet werden. Somit erfolgt vorteilhafterweise nach jedem Aufschließvorgang eine. Neueinstellung des Codes.This has the advantage that any image pattern is selected from the large number of possibilities, for example 24 bits 2 = 16 million. Illegal use of a copied code is practically excluded. Preferably, the Exchange of information of the valid code by means of a forced synchronization, which is achieved, for example, by electronically connecting the transmitter and receiver. This is done, for example, by plugging the transmitter and receiver together in the vehicle so that other functions, for example switching on the ignition, are guaranteed. Thus, one advantageously takes place after each digestion process. Readjustment of the code.
Gemäß einer Weiterbildung der Erfindung sendet der Sender nach einem Batteriewechsel einen Reset-Code, wodurch sichergestellt wird, daß das elektronische Schloß in jedem Fall geöffnet werden kann.According to a development of the invention, the transmitter sends a reset code after a battery change, which ensures that the electronic lock can be opened in any case.
Eine weitere Ausgestaltung sieht vor, daß beim Absinken der Betriebsspannung des Empfängers unter einen bestimmten Wert durch eine Selbsthalte-Schaltung z.B. Relais, ein Riegel betätigt wird, der das Aufschließen mit einem mechanischen Schlüssel ermöglicht.A further embodiment provides that when the operating voltage of the receiver drops below a certain value by means of a latch circuit e.g. Relay, a bolt is operated, which enables unlocking with a mechanical key.
Damit ist sichergestellt, daß ein Kraftfahrzeug auch geöffnet werden kann, wenn beispielsweise vergessen wurde, das Licht auszuschalten, und somit die Batteriespannung nicht mehr zum Betrieb des Empfängers ausreicht.This ensures that a motor vehicle can also be opened if, for example, it has been forgotten to switch off the light and the battery voltage is no longer sufficient to operate the receiver.
Im übrigen kann bei Batteriewechsel im Empfänger ebenfalls mit dem Reset-Code, wie beim Batteriewechsel im Sender, begonnen werden, oder es kann durch eine Zwangssynchronisation der nächstgültige Code des Zufallsgenerators an den Empfänger bzw. an den Sender übermittelt werden.Otherwise, when changing the battery in the receiver, the reset code can also be started, as when changing the battery in the transmitter, or the next-valid code of the random number generator can be transmitted to the receiver or to the transmitter by means of forced synchronization.
Eine weitere Ausführungsform des erfindungsgemäßen Verfahrens besteht darin, daß verschiedene zu einem Empfänger gehörende Sender eine Kennung erhalten, und daß im Empfänger der für jeden Sender gültige Code gespeichert ist. Hierdurch erzielt man den Vorteil, daß beispielsweise für ein Fahrzeug mehrere Schlüssel ausgegeben werden können und gleichzeitig die Vorteile der Codierung mit dem Zufallsgenerator für jeden einzelnen Schlüssel erhalten bleiben.Another embodiment of the method according to the invention is that different to one receiver belonging transmitter receive an identifier, and that the code valid for each transmitter is stored in the receiver. This has the advantage that, for example, several keys can be issued for a vehicle and at the same time the advantages of coding with the random number generator are retained for each individual key.
Es ist auch möglich, daß ein Hersteller, der verschiedene Kunden beliefert, die Schlüsselserie jedes Kunden mit einer bestimmten Kennung versieht, so daß das gleiche Bit-Muster des Codes für verschiedene Kunden anwendbar ist-.It is also possible for a manufacturer who supplies different customers to provide each customer's key series with a specific identifier so that the same bit pattern of the code is applicable to different customers.
Vorzugsweise arbeitet das erfindungsgemäße Verfahren der-. art, daß nur für das Aufsperren die durch den Zufalls-generator ausgewählten Codierungsmöglichkeiten verwendet werden, daß aber für das Zusperren jeweils derselbe Code gesendet wird. Hierzu kann der Sender entweder mit einer Bedien-Taste ausgerüstet sein, welche abwechselnd die Funktionen "auf" bzw. "zu" bedient. Es können aber hierfür auch zwei unterschiedliche Tasten am Sender angeordnet sein. Das Aussenden des Reset-Codes kann beispiels- weise dadurch geschehen, daß eine der Tasten über eine längere Zeit gedrückt wird.The method according to the invention preferably works. Art that the coding options selected by the random generator are only used for unlocking, but that the same code is sent for locking. For this purpose, the transmitter can either be equipped with an operating button which alternately operates the functions "open" and "closed". However, two different buttons can also be arranged on the transmitter for this purpose. The reset code can be sent, for example, by pressing one of the buttons for a long time.
Ein weiterer Vorteil des erfindungsgemäßen Verfahrens besteht beispielsweise darin, daß bei Übergabe des Fahrzeugs in die Werkstatt das Schloß elektronisch geöffnet wird und mit dem mechanischen Schlüssel bedient werden kann, so. daß der elektronische Schlüssel in der Hand des Benutzers bleibt.Another advantage of the method according to the invention is, for example, that when the vehicle is handed over to the workshop, the lock is opened electronically and can be operated with the mechanical key, so. that the electronic key remains in the user's hand.
Eine weitere vorteilhafte Möglichkeit besteht darin, daß sowohl Sender als auch Empfänger mit einer Fortschaltautomatik versehen sind, die den Code zyklisch vertauschen, wenn durch irgendein Versehen die Zwangssynchronisation unterblieben ist. Hierdurch ist sichergestellt, daß ein Kopieren des Codes selbst in dem Fall nichts nutzt, wenn beispielweise nur das Fahrzeug geöffet wird, ohne es in Betrieb zu setzen, so daß eine Zwangssynchronisation nicht stattgefunden hat. In diesem Fall bestünde sonst die Möglichkeit, daß mittels eines kopierten Signals eine unrechtmäßige Benutzung stattfinden-konnte.A further advantageous possibility is that both the transmitter and the receiver are provided with an automatic switching system which cyclically interchange the code, if by any mistake the forced synchronization has not been performed. This ensures that copying the code is of no use even if, for example, only the vehicle is opened without starting it, so that forced synchronization has not taken place. In this case there would otherwise be the possibility that illegal use could take place by means of a copied signal.
Die Kennzeichnung jedes Senders aus der Vielzahl der Sender/Empfänger-Kombinationen läßt sich nach Art eines Auswahlschalters durchführen, der beispielsweise in der DE-U-80 05 555 beschrieben ist. Der Auswahlschalter kann bei der Herstellerfirma aus einem Stempel bestehen, der die entsprechenden Codiereingänge durchtrennt. Auf diese Weise wird ein kennzeichnendes Bildmuster erzeugt, daß bei Initialisierung jeweils gelesen wird, um das Programm an der schlüsselspezifischen Stelle für den Code beginnen zu lassen. Der Kennzeichen-Code ist zweckmäßigerweise gleichzeitig Reset- oder "Tür zu"-Code. Damit ist bei Schlüsselnachbestellung auch eine eindeutige Zuordnung möglich; sie ist bei vergossenem Schlüssel elektronisch durch das Senden des Signals, z.B. "Tür zu", zu ermitteln.The identification of each transmitter from the multitude of transmitter / receiver combinations can be carried out in the manner of a selection switch, which is described, for example, in DE-U-80 05 555. At the manufacturing company, the selection switch can consist of a stamp that cuts through the corresponding coding inputs. In this way, a characteristic image pattern is generated which is read upon initialization in order to have the program start at the key-specific point for the code. The identification code is expediently a reset or "door to" code at the same time. This means that a clear assignment is also possible when reordering keys; when the key is potted, it is electronic by sending the signal, e.g. "Door closed" to determine.
Die Erfindung wird anhand des in der Zeichnung dargestellten Ausführungsbeispieles näher erläutert.The invention is explained in more detail with reference to the embodiment shown in the drawing.
In der einzigen Figur, die ein Blockschaltbild eines elektronischen Schlüssels darstellt, ist mit 1 ein Sender und mit 2 der dazugehörende Empfänger bezeichnet. Zweckmäßigerweise bestehen Sender 1 und Empfänger 2 aus je einem CMOS-Mikroprozessor mit nachfolgendem Verstärker 3 bzw. 7 und Infrarotsendediode 4 bzw. Fototransistor 6. Der Sender 1 sendet über die Fotodiode 4 das codierte Infrarotsignal 5 aus, das vom Fctotransistor 6 empfangen und über den Verstärker 7 dem Empfänger 2 zugeleiter wird. Am Ausgang 8 des Empfängers 2 erscheint ein Steuersignal 9, mit dem die Zentralverriegelung des Kraftfahrzeuges betrieben wird.In the single figure, which shows a block diagram of an electronic key, 1 denotes a transmitter and 2 the associated receiver. Expediently, transmitter 1 and receiver 2 each consist of a CMOS microprocessor with subsequent amplifier 3 or 7 and infrared transmitter diode 4 or
Der für das erfindungsgemäße Verfahren erforderliche Zufallsgenerator läßt sich mit Hilfe der ohnehin-vorhandenen Mikroprozessoren leicht realisieren und entweder im-Sender 1 oder im Empfänger 2 unterbringen.The random generator required for the method according to the invention can be easily implemented with the help of the microprocessors already present and can be accommodated either in the transmitter 1 or in the receiver 2.
Claims (4)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE19823234539 DE3234539A1 (en) | 1982-09-17 | 1982-09-17 | METHOD FOR SECURING THE CODE OF AN ELECTRONIC KEY |
| DE3234539 | 1982-09-17 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0103791A2 true EP0103791A2 (en) | 1984-03-28 |
| EP0103791A3 EP0103791A3 (en) | 1984-09-05 |
Family
ID=6173510
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP83108591A Withdrawn EP0103791A3 (en) | 1982-09-17 | 1983-08-31 | Coding method for an electronic key |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0103791A3 (en) |
| JP (1) | JPS5965175A (en) |
| DE (1) | DE3234539A1 (en) |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0257376A1 (en) * | 1986-08-12 | 1988-03-02 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Electronic locking system comprising at least a lock, particularly for motor cars |
| FR2606232A1 (en) * | 1986-10-31 | 1988-05-06 | Neiman Sa | HIGH-SECURITY EVOLUTIVE ENCODING METHOD AND DEVICE FOR IMPLEMENTING SAID METHOD |
| FR2640104A1 (en) * | 1988-12-03 | 1990-06-08 | Hella Kg Hueck & Co | DEVICE FOR REMOTE CONTROL OF SECURITY MEANS SUCH AS CENTRALIZED LOCKINGS AND ANTI-THEFT SECURITIES |
| GB2226593A (en) * | 1988-12-30 | 1990-07-04 | Ivan Anastasovski | Digital electronic lock |
| DE9419635U1 (en) * | 1994-12-09 | 1995-03-02 | Engel Gerhard Dipl Ing | Safety device, in particular for motor vehicles |
| DE4440349A1 (en) * | 1994-11-11 | 1996-05-15 | Bayerische Motoren Werke Ag | Method for synchronizing two dialog-capable transceiver units for a code signal in a motor vehicle locking system |
| DE19533732A1 (en) * | 1995-09-12 | 1997-03-13 | Koerling Franz Josef | Electronic protection system for preventing unauthorised access to locked door or cover |
| FR2738587A1 (en) * | 1995-09-08 | 1997-03-14 | Kiekert Ag | Operation of lock for car using remote control device |
Families Citing this family (18)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| USRE35364E (en) | 1985-10-29 | 1996-10-29 | The Chamberlain Group, Inc. | Coding system for multiple transmitters and a single receiver for a garage door opener |
| DE3421540A1 (en) * | 1984-06-08 | 1986-01-02 | Audi AG, 8070 Ingolstadt | Closing system having a battery-operated infrared hand-held transmitter |
| JPH07961B2 (en) * | 1985-10-16 | 1995-01-11 | カシオ計算機株式会社 | Electronic key device |
| JPS62101771A (en) * | 1985-10-29 | 1987-05-12 | オムロン株式会社 | Remote control type key operation apparatus |
| JPH01244088A (en) * | 1988-03-22 | 1989-09-28 | Kondeishiyonaru Akusesu Technol Kenkyusho:Kk | Electronic lock |
| AT395998B (en) * | 1991-09-09 | 1993-04-26 | Grundmann Gmbh Geb | Arrangement for power and data transmission |
| DE4411449C1 (en) * | 1994-04-01 | 1995-03-16 | Daimler Benz Ag | Vehicle security device with electronic use-authorisation coding |
| DE4411450C1 (en) * | 1994-04-01 | 1995-03-30 | Daimler Benz Ag | Vehicle security device with electronic use authorisation encoding |
| DE4411451C1 (en) * | 1994-04-01 | 1995-05-04 | Daimler Benz Ag | Vehicle security device with electronic use authorisation encoding |
| BR9606663A (en) | 1995-05-17 | 1997-09-16 | Chamberlain Group Inc | Transmitter to send an encrypted signal to control a receiver actuator to receive an encrypted signal from a transmitter and to generate an actuation signal and receiver to receive an encrypted radio frequency signal from a transmitter and to generate an actuation signal |
| US6980655B2 (en) | 2000-01-21 | 2005-12-27 | The Chamberlain Group, Inc. | Rolling code security system |
| US6690796B1 (en) | 1995-05-17 | 2004-02-10 | The Chamberlain Group, Inc. | Rolling code security system |
| US8422667B2 (en) | 2005-01-27 | 2013-04-16 | The Chamberlain Group, Inc. | Method and apparatus to facilitate transmission of an encrypted rolling code |
| US9148409B2 (en) | 2005-06-30 | 2015-09-29 | The Chamberlain Group, Inc. | Method and apparatus to facilitate message transmission and reception using different transmission characteristics |
| US10652743B2 (en) | 2017-12-21 | 2020-05-12 | The Chamberlain Group, Inc. | Security system for a moveable barrier operator |
| US11074773B1 (en) | 2018-06-27 | 2021-07-27 | The Chamberlain Group, Inc. | Network-based control of movable barrier operators for autonomous vehicles |
| US11423717B2 (en) | 2018-08-01 | 2022-08-23 | The Chamberlain Group Llc | Movable barrier operator and transmitter pairing over a network |
| US10997810B2 (en) | 2019-05-16 | 2021-05-04 | The Chamberlain Group, Inc. | In-vehicle transmitter training |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3859634A (en) * | 1971-04-09 | 1975-01-07 | Little Inc A | Digital lock system having electronic key card |
| US4148092A (en) * | 1977-08-04 | 1979-04-03 | Ricky Martin | Electronic combination door lock with dead bolt sensing means |
| FR2420008A1 (en) * | 1978-03-17 | 1979-10-12 | Neiman Sa | MOTOR VEHICLE LOCK CONTROL DEVICE |
| DE2824421A1 (en) * | 1978-06-03 | 1979-12-13 | Bosch Gmbh Robert | SWITCH ARRANGEMENT FOR ELECTRONIC LOCKING OR UNLOCKING OF SAFETY DEVICES, IN PARTICULAR AS THEFT PROTECTION IN A MOTOR VEHICLE |
| GB1595797A (en) * | 1978-04-21 | 1981-08-19 | Pushman Hugh John | Security systems |
| DE3006128A1 (en) * | 1980-02-19 | 1981-08-20 | Sachs Systemtechnik Gmbh, 8720 Schweinfurt | Electric lock-up system with key and variable secret code - converts code into signal for comparison with changeable stored code producing switching signal |
-
1982
- 1982-09-17 DE DE19823234539 patent/DE3234539A1/en not_active Withdrawn
-
1983
- 1983-08-31 EP EP83108591A patent/EP0103791A3/en not_active Withdrawn
- 1983-09-12 JP JP58168095A patent/JPS5965175A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3859634A (en) * | 1971-04-09 | 1975-01-07 | Little Inc A | Digital lock system having electronic key card |
| US4148092A (en) * | 1977-08-04 | 1979-04-03 | Ricky Martin | Electronic combination door lock with dead bolt sensing means |
| FR2420008A1 (en) * | 1978-03-17 | 1979-10-12 | Neiman Sa | MOTOR VEHICLE LOCK CONTROL DEVICE |
| GB1595797A (en) * | 1978-04-21 | 1981-08-19 | Pushman Hugh John | Security systems |
| DE2824421A1 (en) * | 1978-06-03 | 1979-12-13 | Bosch Gmbh Robert | SWITCH ARRANGEMENT FOR ELECTRONIC LOCKING OR UNLOCKING OF SAFETY DEVICES, IN PARTICULAR AS THEFT PROTECTION IN A MOTOR VEHICLE |
| DE3006128A1 (en) * | 1980-02-19 | 1981-08-20 | Sachs Systemtechnik Gmbh, 8720 Schweinfurt | Electric lock-up system with key and variable secret code - converts code into signal for comparison with changeable stored code producing switching signal |
Cited By (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0257376A1 (en) * | 1986-08-12 | 1988-03-02 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Electronic locking system comprising at least a lock, particularly for motor cars |
| FR2606232A1 (en) * | 1986-10-31 | 1988-05-06 | Neiman Sa | HIGH-SECURITY EVOLUTIVE ENCODING METHOD AND DEVICE FOR IMPLEMENTING SAID METHOD |
| EP0269862A1 (en) * | 1986-10-31 | 1988-06-08 | Valeo Neiman | Evolutive high-security coding method |
| FR2640104A1 (en) * | 1988-12-03 | 1990-06-08 | Hella Kg Hueck & Co | DEVICE FOR REMOTE CONTROL OF SECURITY MEANS SUCH AS CENTRALIZED LOCKINGS AND ANTI-THEFT SECURITIES |
| GB2226593A (en) * | 1988-12-30 | 1990-07-04 | Ivan Anastasovski | Digital electronic lock |
| DE4440349A1 (en) * | 1994-11-11 | 1996-05-15 | Bayerische Motoren Werke Ag | Method for synchronizing two dialog-capable transceiver units for a code signal in a motor vehicle locking system |
| DE9419635U1 (en) * | 1994-12-09 | 1995-03-02 | Engel Gerhard Dipl Ing | Safety device, in particular for motor vehicles |
| FR2738587A1 (en) * | 1995-09-08 | 1997-03-14 | Kiekert Ag | Operation of lock for car using remote control device |
| DE19533732A1 (en) * | 1995-09-12 | 1997-03-13 | Koerling Franz Josef | Electronic protection system for preventing unauthorised access to locked door or cover |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| DE3234539A1 (en) | 1984-03-22 |
| EP0103791A3 (en) | 1984-09-05 |
| JPS5965175A (en) | 1984-04-13 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0103791A2 (en) | Coding method for an electronic key | |
| DE3905651C2 (en) | ||
| EP0212046B1 (en) | System for locking and/or unlocking a security device | |
| DE19533195B4 (en) | Method for operating a locking device for a motor vehicle with a remote control device and with a transponder | |
| EP0106273B1 (en) | Safety device | |
| DE4438276B4 (en) | Method for operating a door lock and unlocking | |
| DE60109811T2 (en) | Remote control device and method for configuring such a remote control device | |
| DE3712552C2 (en) | ||
| DE19622720C2 (en) | Authentication facility with key number memory | |
| DE3327720A1 (en) | METHOD AND DEVICE FOR OPERATING AN ELECTRONIC SAFETY DEVICE | |
| EP0809743A1 (en) | Electronic key | |
| DE4409559A1 (en) | Key for car central door locking system | |
| WO1995009746A1 (en) | Locking system, in particular for motor vehicles | |
| DE3532156C2 (en) | ||
| EP1302374B1 (en) | Method of initialising an entry control system with several electronic keys and several objects | |
| DE10136035A1 (en) | Electronic control system using a single receiver for different control modes | |
| DE3503177A1 (en) | PROGRAMMABLE ELECTRONIC LOCK | |
| DE4300127A1 (en) | ||
| WO1994018036A1 (en) | Remote-controlled protection system for a motor vehicle | |
| EP0103790A2 (en) | Coding method for an electronic key | |
| EP0257212A2 (en) | Central locking system for a motor vehicle | |
| EP0154019A1 (en) | Coding method for an electronic key | |
| DE4433499C2 (en) | Electronic anti-theft protection system for a motor vehicle | |
| EP0761917A1 (en) | Key for motor vehicle | |
| DE10112573C2 (en) | Method for initializing an anti-theft system for a motor vehicle |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): AT DE FR GB IT SE |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): AT DE FR GB IT SE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19841026 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE APPLICATION HAS BEEN WITHDRAWN |
|
| 18W | Application withdrawn |
Withdrawal date: 19850823 |
|
| RIN1 | Information on inventor provided before grant (corrected) |
Inventor name: HAGEDORN, HORST, DIPL.-ASTR. Inventor name: PREISSINGER, HEINZ, DIPL.-PHYS. Inventor name: HEUWIESER, ERWIN, DIPL.-ING. |